Kantar publishes the annual results of the Africascope 2019
TV, Radio, and Internet study,
which covers
the main
cities
in
eight sub-Saharan African
countries:
Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Côte d'Ivoire, Gabon, Mali, Democratic Republic of Congo,
Republic of Congo, and Senegal, representing a total
of
19.1
million individuals aged 15 and over (January-December 2019)
.
The interviews were conducted face-to-face on tablets with a total sample of 17,000 people
, representative of the population
aged 15 and over
in the survey area.
MAIN FINDINGS 1/ Very high media exposure. An average of 6 hours and 12 minutes per day
is spent watching television,
listening to the radio,
browsing the Internet,
or reading the press.
This average time spent
on media
has increased by 4 minutes compared to the previous wave.
Nearly two-thirds of media exposure time is captured by television.
In 2019, 92% of
Africans watched television
on a daily basis,
representing
17.5
million viewers each day.
On average,
they watched television for 3 hours and 55 minutes each day.
Managers and executives
spend nearly 9 hours consuming media, with television accounting for 53% of their media consumption time, while radio and the internet are at the same level with 22% and 24% respectively.
More than 60% of the time spent in front of the small screen by those aged 15 and over is spent watching international and pan-African channels. However, national channels enjoy very high daily coverage and occupy the top spots among the channels with the most viewers.
Details of total TV viewing time and top 3 daily audience ratings by country:

2/ A migration to DTT that is gaining ground
While the deadline set by the International Telecommunication Union for the definitive switch to DTT in
June 2020 will be difficult for some
countries to meet, awareness and intention to purchase indicators show
that
things are moving in the right direction.
In French-speaking Africa, 63% of individuals have already heard of DTT (+11 points vs. the first
half of 2019). It is in Côte d'Ivoire and the DRC
that
awareness of DTT is growing the most.
Fifty-eight percent of
those without equipment are
considering switching to DTT
(+10 points vs. the first
half of 2019). Here
again, the strongest growth is in Côte d'Ivoire and the DRC.
The main motivation is, of course, access to new channels
(57% of those planning to switch), better sound and image quality (28%), and fewer interruptions in the event of rain, for example (11%).
In Burkina Faso, the first
country to have officially
completed the migration
to digital signal in
November 2019, 53% of households
receive television via DTT. The figure is 14% in Senegal and 10% in the DRC.
3/ A quarter of media exposure is devoted to listening to the radio
The
share of daily listeners, although slightly down
from previous waves,
appears to be stabilizing. In 2019,
62%
of individuals aged 15 and over
listened to the radio
every day. They spent an
average of 1 hour and 29 minutes
per day listening.
Details of total radio listening times and top 3 audience ratings by country:
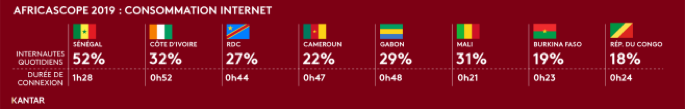
4/ Internet use continues to grow, with an average of 47 minutes per day
The average time spent on the Internet
varies greatly from one country to another.
Every day, 29% of people go online (+4 points vs. 2018). The proportion of daily Internet users is increasing in all countries measured, with the exception of Cameroon and the DRC, where it remains stable.
Details of Internet user share and average daily connection time by country:
TV & Radio audience indicators – Definitions: Cumulative audience (CA): Number or percentage of individuals who listened to a radio station or watched a television channel at any time during the day, regardless of duration.
Audience share (AS) as a percentage: Share of the total viewing time for television/radio media represented by the viewing time for a channel/station. The sum of the audience shares for all media is equal to 100%.
Listening time per individual (DEI): Average time spent listening to programs broadcast by television channels/radio stations by all individuals in the population studied.

